Opportunity Discovery
Overview
- Identify a problem worth solving using Jobs-to-be-Done (JTBD) methodology
- Empathize with the customer to further define the problem using Design Thinking
- Use Brainstorming to think of solutions for your idea
- Do a quick Back-of-the-Envelope calculation exercise to find out the viability of your idea
Session 1: Identify a Problem Worth Solving - I(CORE) - 2 Item[s]
Where should I start?
- Solution
- Product
- Idea
- Customer
Entrepreneurs see problems as opportunities
CUSTOMER: Opportunities are not always disguised as problems, sometimes they can be found around a group of people or the customer. For example: Pregnant women - Get them bio-engineerred smelling salt (Keep nausea at bay and Vitamin D at optimum)
Problem: A job that someone is unable to do or does with a lot of friction.
Where to look?
- Existing products
- Alternatives
- Pain points
- Friction
Ex: Problem- Vacuum cleaner constantly get clogged and lose suction. Solution- Dyson built dyson vacuum cleaner (a bagless vacuum that does not lose suction) after 500 failed attempts
Anticipate future problem
- Based on current trends, structural changes, and predict problems.
But first make sure if the problem is really worth solving. Will people pay? Steps:
- Observe, observe, observe - Look for a job they are truying to get done.
- Empathize while observing - To see what the point of friction is.
- Find out the trigger pushing the customer to look for a change (Vacuum cleaner getting clogged and losing suction)
- Focus on existing alternative - Would the customers be better off with existing alternatives?
- What jobs customer wants done by hiring the product.
- Validate them from horses mouth (your customers)
! [[ 31225561_1609400863.pdf ]]
Session 2: Identify a Problem Worth Solving - II (CORE)
! [[ 31225776_1609401010.pdf ]]
Session 3: Design Thinking (CORE) - 7 Item[s]
Harnessing creativity to: - Make something of value - Solve problems - Change the world is Design!
Design is not just how things look like or how things feel like, but how things work. - Steve Jobs
What is Design Thinking? It is taking the way designer’s method of thinking and working, and applying it to different problems.
Process:
-
Deeply human-centered
- Understand their needs and wishes
-
Identifying an opportunity of improvement
- Solution-focussed
- What is => What can be (Action-oriented)
-
Building up of ideas
- Opposed to learning from the past
- Thinking wildly and Testing rapidly
- Creating multiple solutions
Design Thinking = Empathy + Imagination + Intuition + Obductive reasoning (to explore possibililites to benefit the end-user.)
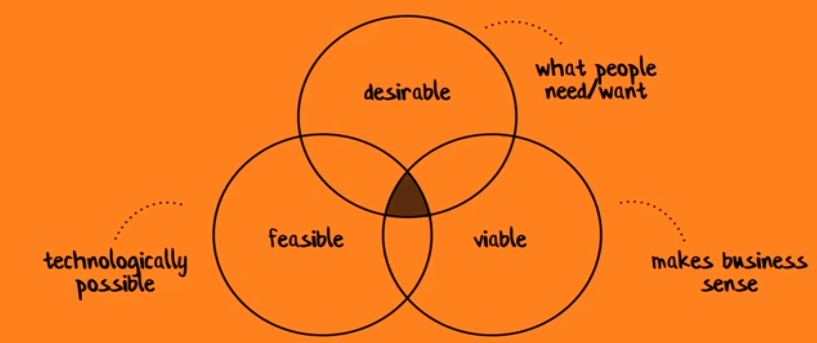
Values of Design Thinking:
- Empathy: Walk in the shoes of your users.
- Curiousity: Investigate everything.
- Imagination: Let your imagination play.
- Making: Make <=> Break <=> Iterate (Keep experiment; Shape and refine ideas)
- Optimism: Frame problems into opportunity.
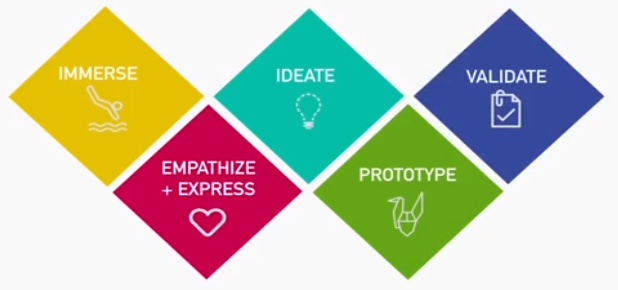
Popular Models of Design Thinking
- STANFORD d.school
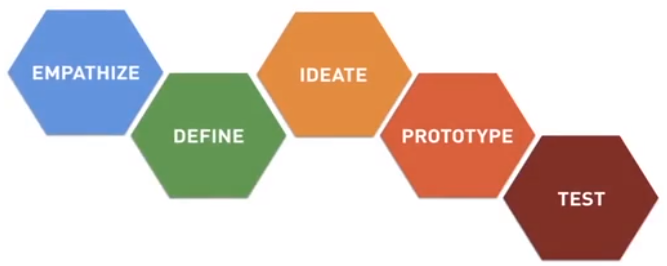
- Design Thinking for Educators: Toolkit

- Design Minds: DT Process
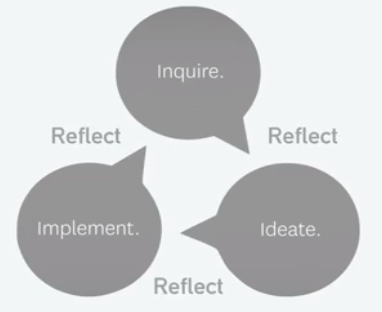
- Washwani Foundation Design Thinking
! [[ 24431295_1592465369.pdf ]]
Session 4: Look for Solutions (CORE) - 3 Item[s]
Brainstorming: Group creativity technique for idea generation. Allows free flows of ideas and thoughts within a short frame of time.
- Generate as many ideas as possible
- Don’t criticize anyone or anyone’s idea
- Welcome wild and crazy ideas
- Build upon each others’ ideas
! [[ 24431971_1592465462.pdf ]]